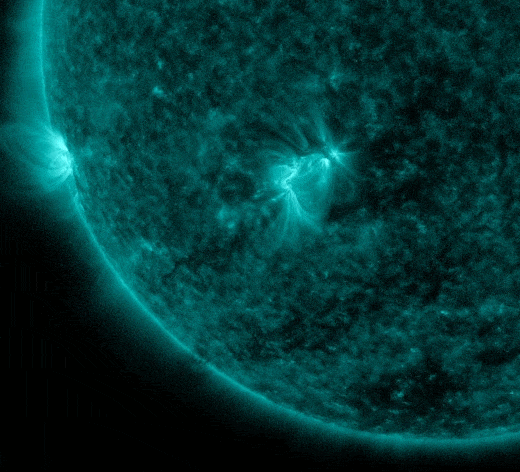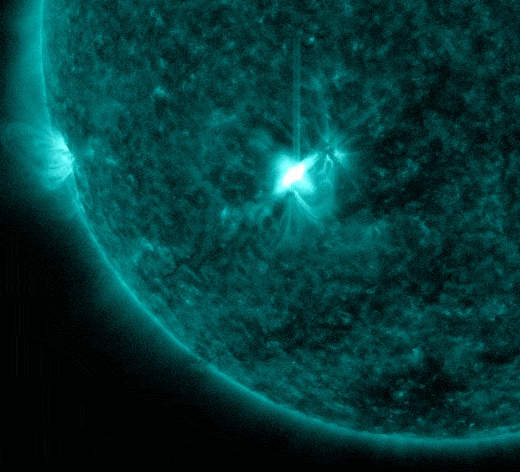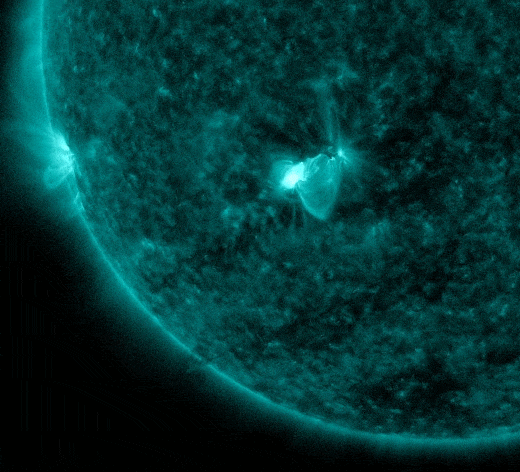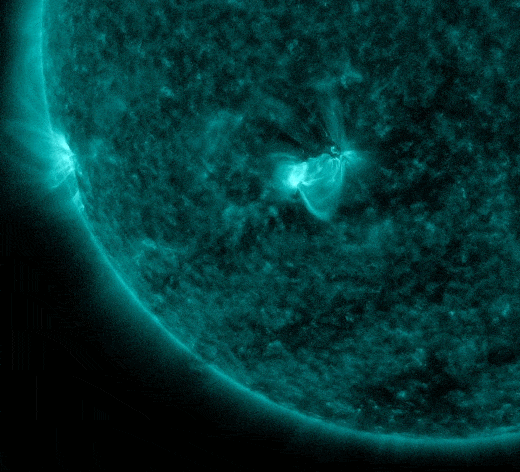
Our Star is waking up from it's long hibernation: Sunspot AR2816 erupted during the late hours of April 19th (2342 UT), producing a strong M1-class solar flare, one of the biggest of the infant Solar Cycle 25 which began in December 2019. Solar Cycle 25 is expected to continue until about 2030. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory recorded the extreme ultraviolet flash: Solar Cycle 24 is the most recently completed solar cycle, the 24th since 1755, when extensive recording of solar sunspot activity began.
It began in December 2008 with a smoothed minimum sunspot number of 2.2, and ended in December 2019. Activity was minimal until early 2010.Solar Cycle 24 reached its maximum in April 2014 with a 23 months smoothed sunspot number of 81.8. This maximum value was substantially lower than other recent solar cycles, down to a level which had not been seen since cycles 12 to 15 which occured in (1878-1923).
According to Spaceweather this is one of the strongest flares of young Solar Cycle 25. A pulse of X-rays and ultraviolet radiation from the flare ionized the top of Earth's atmosphere, causing a shortwave radio blackout over the Pacific Ocean: blackout map. Mariners and ham radio operators in the area might have noticed unusual propagation at frequencies below ~20 MHz.
Interestingly, during the radio blackout the sun generated its own burst of radio noise. Shock waves from the solar flare rippled through the sun's atmosphere, creating plasma instabilities and natural radio emissions; NOAA reports the detection of Type II and Type IV bursts. These radio bursts may have penetrated the blackout, causing roars of static in the loudspeakers of shortwave radios at the same time that normal terrestrial signals were suppressed. Research shows that solar radio bursts can interfere with the navigation of whales.
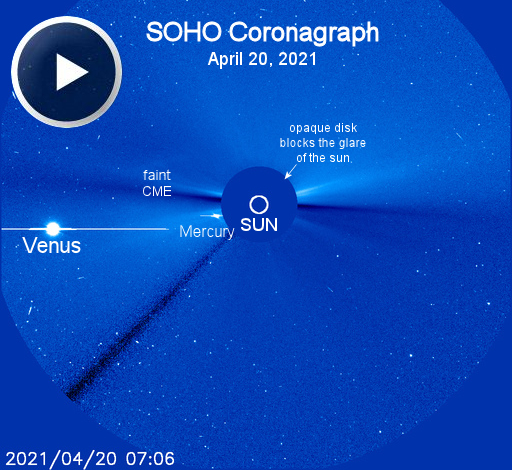
The explosion also hurled a coronal mass ejection (CME) into space. In this SOHO coronagraph movie, watch Mercury emerge from behind the occulting disk at about the same time as the CME:
UPDATE: Using these images, NOAA analysts have modeled the CME and determined that it will not hit Earth. Auroraphiles may be disappointed, but here's some good news: With the increasing pace of solar activity, it's only a matter of time before the sun sends a CME in our direction. Stay tuned.
No comments:
Post a Comment